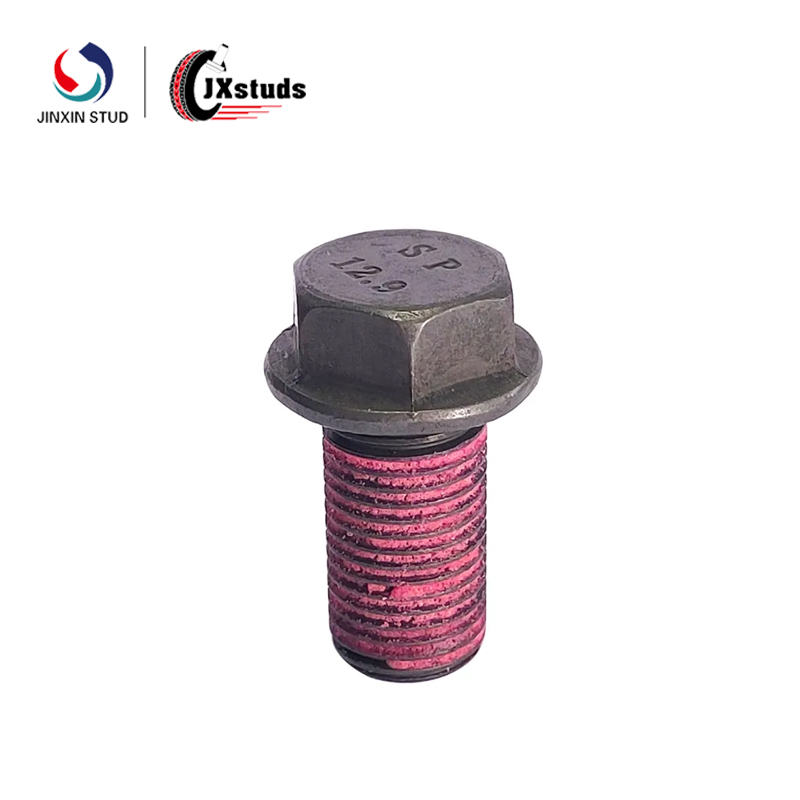
Forming is a crucial process in the metalworking and manufacturing industries. Whether it's automotive parts, aerospace components, or everyday fasteners like screws and nuts, forming technology is essential.
Thermoforming and cold forming are the two most common methods. Many engineers and purchasers ask: What's the difference between the two? How do you choose between them?
What is thermoforming?
Thermoforming is a process in which metal is heated to a high temperature and then plastically processed.
Process flow: Heating → Forming → Cooling
Common applications: Automotive body parts, large structural components, complex aerospace parts
Advantages:
Easier to form complex shapes
Reduced risk of work hardening
Suitable for processing high-strength materials
Disadvantages:
High energy consumption
Relatively short mold life
Relatively higher costs
What is cold forming?
Cold forming is a forming process performed at or near room temperature. Process Flow: Raw Material Preparation → Forming → Heat Treatment (Optional)
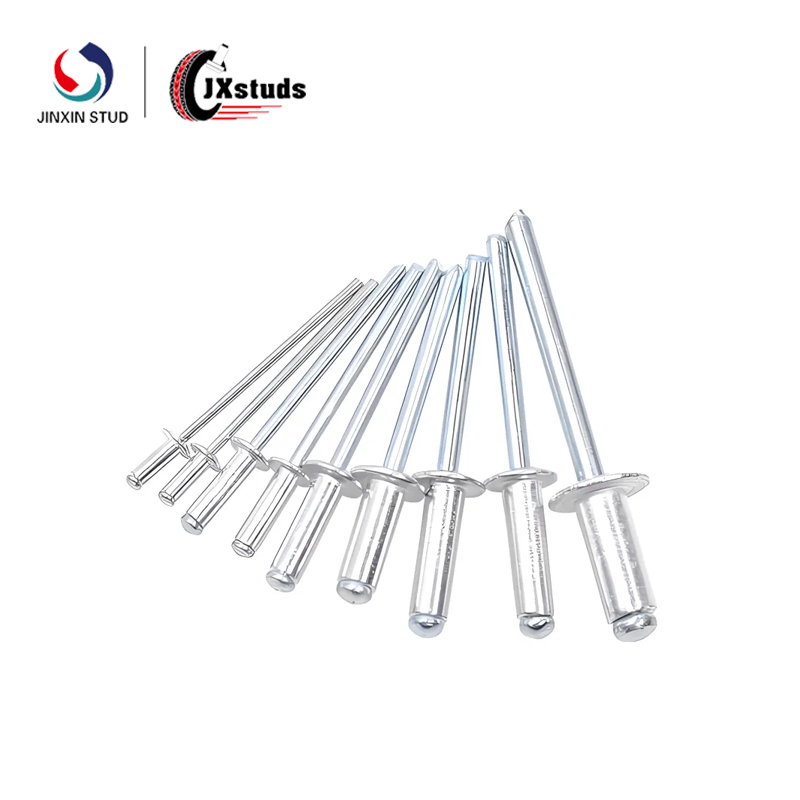
Common Applications: Screws, nuts, nails, small fasteners, precision parts
Advantages:
Good surface quality and high dimensional accuracy
High finished product strength (work hardening effect)
High process efficiency, suitable for large-scale production
Disadvantages:
Limited deformation
Unsuitable for overly complex or large workpieces
How to Choose the Appropriate Forming Process?
When deciding between thermoforming and cold forming, consider the following:
Part Size and Shape: Complex, large parts → hot forming; small, standard parts → cold forming.
Material Properties: High-strength, hard-to-deform alloys → hot forming; ductile metals → cold forming.
Cost and Volume Requirements: Limited budget and high-volume production → cold forming is more advantageous.
Industry Application Requirements: Thermoforming is commonly used for aerospace and automotive structural parts; cold forming is predominant in the fastener industry.
In actual production, these two processes are not mutually exclusive. Instead, they need to be selected based on specific product requirements, material characteristics, and budget, and can even be used in combination. If you are looking for reliable forming process solutions or related products (such as high-performance tungsten alloy parts and fasteners), please feel free to contact us for professional support and customized quotes.