Screws and Bolts are common fasteners that are used in a wide range of applications such as machine building, construction work, electronic equipment and furniture assembly. However, many people tend to confuse the difference between the two.
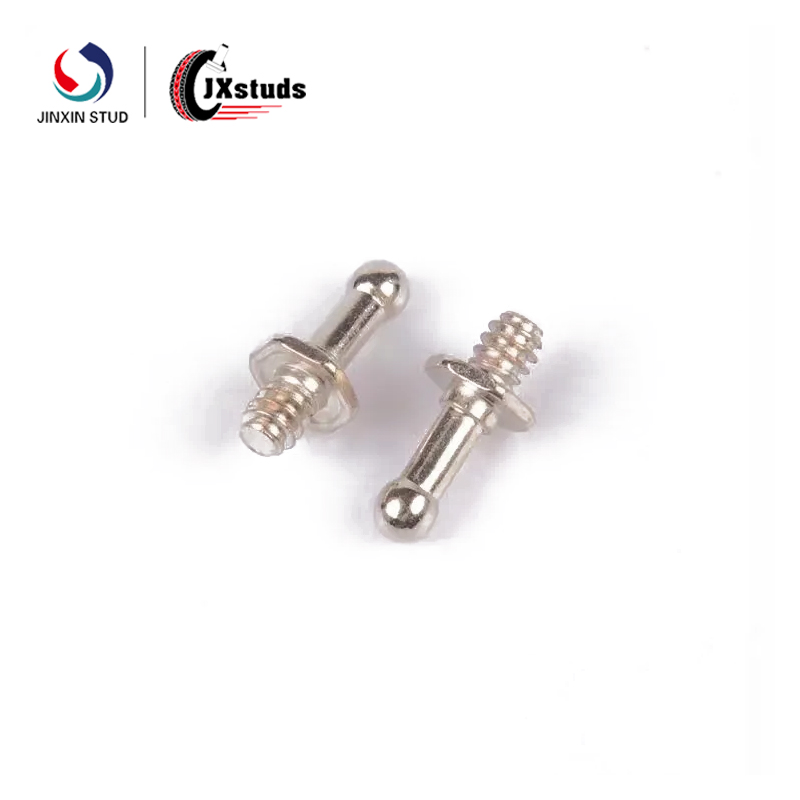
Screws are self-threaded fasteners that usually do not require an additional nut, but are screwed directly into the material to be secured, such as wood, plastic, metal, etc.
Key features of screws
The threads are usually finer and provide a stronger bite.
Most screws have slots in the head such as Phillips, Hex, and Plum, and need to be tightened with a screwdriver or power tool.
Commonly used in electronics, household appliances, furniture, building decoration and other scenarios.

Common Screw Types
✅ Self-tapping screws: can be tapped by themselves to form internal threads, suitable for metal, plastic, wood.
✅ Machine Screws: for precision equipment, electronic products, usually with nuts or internal threaded holes.
✅ Wood Screws: Specialized for wood, with deeper threads to increase fixing power.
✅ Self-drilling Screws: with a drill tip that penetrates directly into metal or wood panels without pre-drilling.
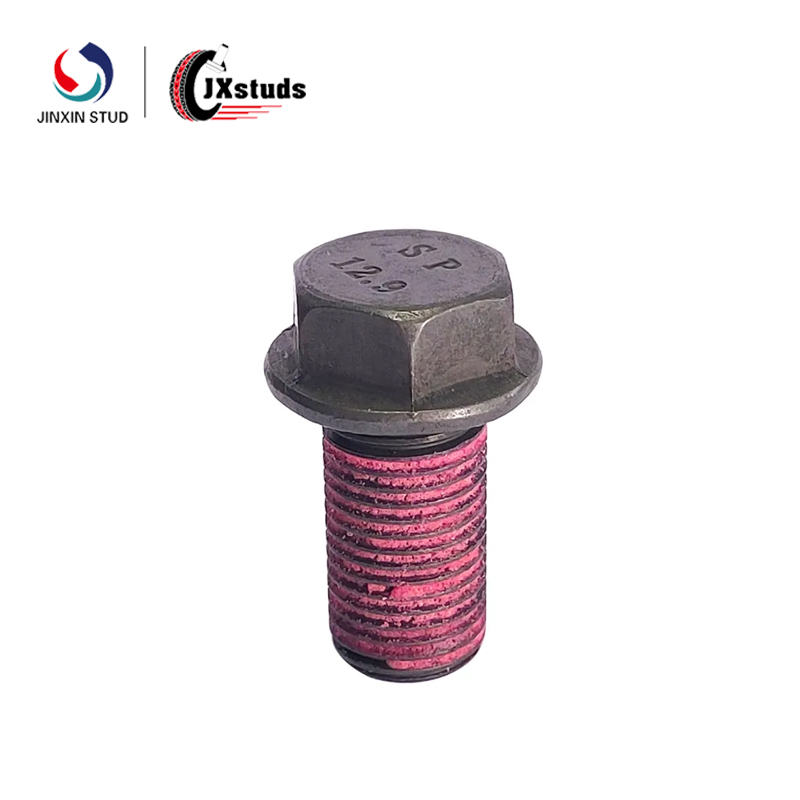
A bolt is a fastener with an external thread that must be used with a nut to securely join two or more parts together.
Main characteristics of bolts
Suitable for high-strength connections and can withstand large tensile and shear forces.
Generally the head is hexagonal head, round head or square head, and need wrench or socket tool to tighten.
Widely used in machinery manufacturing, construction engineering, automotive industry, bridges and steel structures.

Common bolt types
✅ Hexagon Head Bolts (Hex Bolts): the most common type of bolts in industrial manufacturing, suitable for steel structures, mechanical assembly.
✅ Expansion Bolts: suitable for concrete walls, fixed installation in building construction.
✅ T-bolts: used in aluminum framing, sliding installation in T-slots.
✅ U-bolts: commonly used for fixing cylindrical objects such as pipes, frames and so on.