Bolts and nuts are indispensable fasteners in mechanical engineering and construction. By working in conjunction with each other, they form a solid connection that ensures the stability and safety of the structure.
1. Ordinary bolts: usually with hexagonal head and smooth or threaded body. Widely used in a variety of mechanical structures and daily necessities, such as furniture assembly and small equipment. 2.
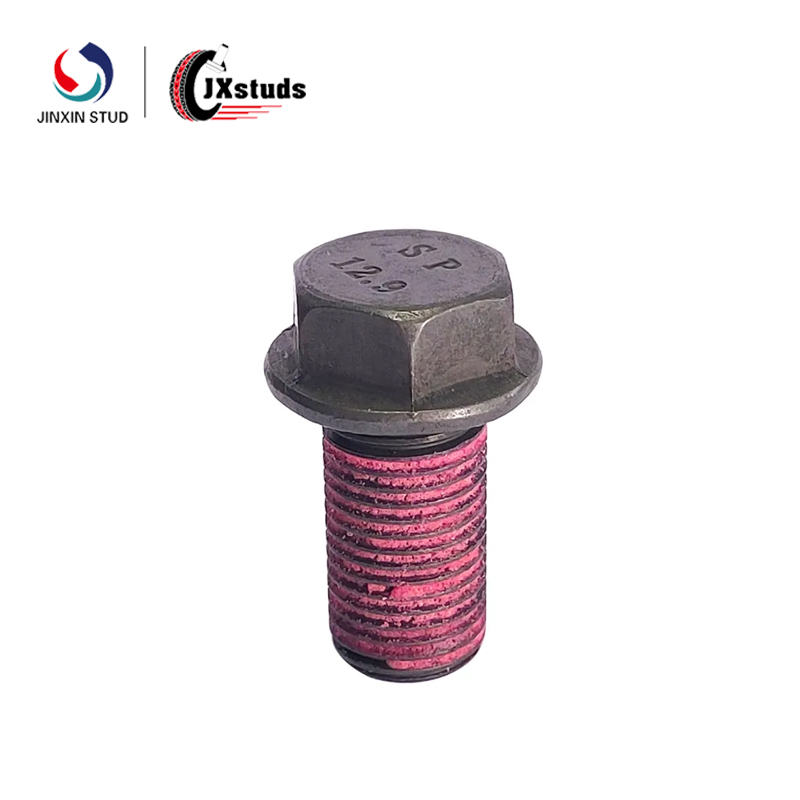
2. High-strength bolts: made of high-strength materials, usually after special treatment to enhance its load-bearing capacity. Mainly used for occasions with large loads, such as construction, bridges and heavy machinery.
3. anti-loosening bolts: designed with anti-loosening structures, such as lock washers or self-locking nuts. Suitable for environments with high vibration, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
4. flange bolts: head with flange, can provide a larger contact area. Used where greater connection strength is required, such as piping and equipment connections. 5.
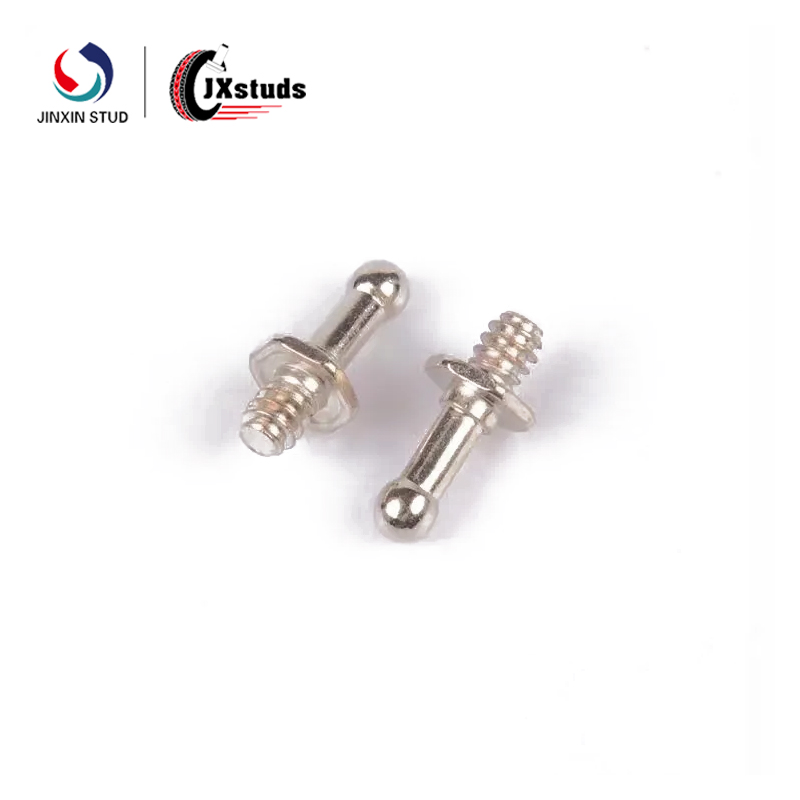
5. Ring bolts: have one or more ring-shaped protrusions. Used in situations that require mounting or traction, such as lifting and transporting equipment.
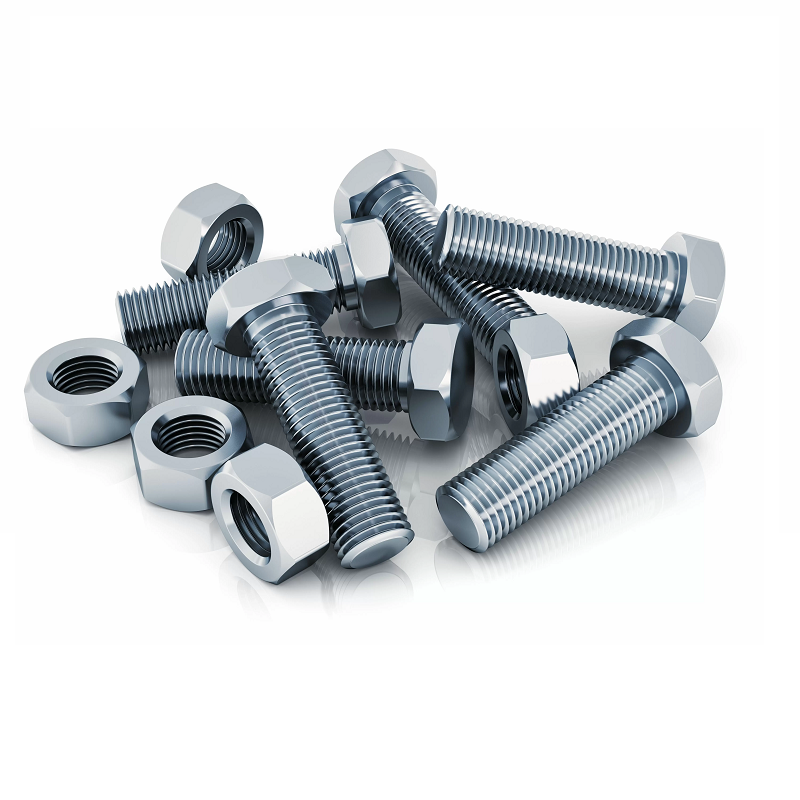

1. Hexagonal Nuts: Standard hexagonal design for easy tightening with a wrench. Suitable for a variety of mechanical and construction applications, it is the most common type of nut.
2. Lock Nuts: With internal anti-loosening structure, such as nylon ring or serrated design. Suitable for high vibration environments and can effectively prevent loosening.
3. Circular nuts: round design, usually used in applications where symmetry is required. Used in some specific machinery to provide uniform force.
4. Square Nut: Square design, easy to use in small space. Commonly used in specific machinery or for special installation requirements.
5. Nut Washers: Washers are added between the nut and the connecting surface to distribute the pressure. Suitable for applications where increased friction and dispersion of forces are required.